Abstract

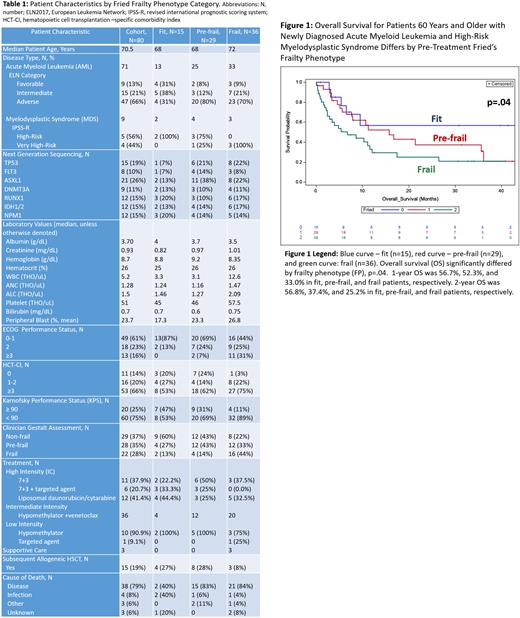
Introduction: Older patients with high-grade myeloid neoplasms may be eligible for treatments of varying intensity, ranging from single agent targeted therapy to intensive induction chemotherapy (IC). Even in patients of similar age, predicting treatment toxicity and remission is difficult due to heterogeneity in comorbidities, physiological reserves, and disease features. Current methods used to assess a patient's fitness for treatment are the ECOG performance status, subjective clinician conjectures (i.e. clinician gestalt, CG), and often age itself. None of these assessments include objective measures. Tools to predict physiological reserve are needed to improve risk stratification of older adults. The Fried frailty phenotype (FP) uses both subjective (exhaustion, reported weight loss, and activity level) and objective measures (gait speed and grip strength) to categorize patients into fit, pre-frail, and frail and can be performed by any member of the medical team in fifteen minutes. We hypothesized that pre-treatment FP would correlate with early overall mortality (OM, death from any cause) and 2-year overall survival (OS) in older patients with myeloid diseases undergoing initial therapy and could be used, alongside disease characteristics, to guide treatment selection. Methods: From September, 2018 to May, 2022 we prospectively enrolled 80 patients age 60 years or older with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) on an IRB approved clinical trial. We performed FP, hematopoietic cell transplantation-comorbidity index (HCT-CI), Karnofsky performance status (KPS), ECOG, and recorded clinician gestalt fitness status (fit or unfit AND frail, non-frail, or pre-frail) on all patients prior to initiation of any disease-directed therapy. Results: The median age was 70.5 (range 60-91) years. Most patients had high-risk disease features, with 66% of AML patients being adverse risk by ELN2017 and all MDS patients having high or very high-risk disease by the IPSS-R. The most common diseases-associated mutations were in TP53, FLT3, ASXL1, DNMT3A, RUNX1, IDH1/2, and NPM1. By FP assessments, 19% of patients were fit (score 0, n=15), 36% were pre-frail (score 1-2, n=29), and 45% were frail (score 3-5, n=36). The majority of patients had HCT-CI scores ≥3 (66%) and KPS <90 (75%). Most patients had low ECOG scores (0-2, 66%), including 44% categorized as frail by FP. By CG, 37% of patients were rated as non-frail (n=36), eight of whom (22%) were frail by FP. Treatment consisted of high intensity IC (7+3 +/- targeted agent or liposomal daunorubicin/cytarabine) in 36%, intermediate intensity (hypomethylating agent + venetoclax, HMA/ven) in 45%, low intensity (HMA or single agent targeted therapy) in 14%, and best supportive care in 4%. 60% of fit patients, 41% of pre-frail patients, and 22% of frail patients received high intensity IC. Subsequent treatment included allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in 27% of fit patients, 28% of pre-frail patients, and 8% of frail patients. For the entire cohort, 60-day and 100-day OM rates were 14.1% and 24.8%, respectively. FP was significantly associated with OM and OS (Figure 1; p=.04). 60-day OM was 25% for frail patients, 7% for pre-frail patients and 0% for fit patients. 100-day OM was 37% for frail patients and 15% for both pre-frail and frail patients. 2-year OS was 56.8%, 37.4%, and 25.2% in fit, pre-frail, and frail patients. In addition, creatinine at baseline >1.3 (p=.03), higher ECOG score (p=.002) and presence of a TP53 mutation (p=.03), were significantly associated with inferior OS. However, none of the other metrics assessed, including WBC at baseline, non-TP53 mutations, CG assessment, or HCT-CI were associated with OS. Conclusion: In newly diagnosed older patients with aggressive myeloid neoplasms, 45% are frail by FP at baseline. Frail status by FP was significantly associated with a high early OM and inferior OS. Pre-frail patients had similar 100-day OM to fit patients, but worse OS by 2 years. Our work indicates that incorporating objective measures of fitness, such as FP, rather than relying solely on a clinician's instincts or a patient's co-morbidity score, may improve risk stratification of newly diagnosed older patients with aggressive myeloid neoplasms. Whether prospective FP can be used to select treatment intensity to improve outcomes will be evaluated in our future work.
Disclosures
Perl:Astellas, Daiichi Sankyo, Abbvie, Genentech, BerGenBio, Immunogen, BMS/Celgene, Actinium: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas, Daiichi Sankyo, AbbVie, Forma, Sumitomo Dainippon, BeatAML LLC, Loxo, LLS/Beat AML, Forma, New Link Genetics, Bayer, Biomed Valley Discoveries: Consultancy; Astellas, Abbvie, Daiichi Sankyo, FujiFilm, Syndax: Research Funding. Gill:Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Honoraria; Hemogenyx: Honoraria, Research Funding; Asher Bio: Research Funding; Interius: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Research Funding; Carisma: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Research Funding; Immpact Bio: Honoraria; Mission Bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Babushok:Carisma Therapeutics: Current equity holder in private company; PHAR, LLC: Consultancy. Hexner:PharmaEssentia: Consultancy; Tmunity Therapeutics: Research Funding; American Board of Internal Medicine: Other: Member of the hematology exam committee; Blueprint Medicines Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Samus Therapeutics, Novartis Oncology: Research Funding. Frey:Novartis: Research Funding; Sana Biotechnology, Kite Pharma, and Syndax Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Lai:AbbVie, Agios/Servier, Daiichi-Sankyo, Jazz, Macrogenics, PDS, Pfizer, Genentech, Taiho, Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas, Jazz: Speakers Bureau. Porter:Wiley: Honoraria; Tmunity Therapeutics: Patents & Royalties: anti-CD19 CART; Bluebird Bio: Consultancy; Angiocrine: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; DeCART: Consultancy; Kite/Gilead: Consultancy; Kadmon: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties: anti-CD19 CART, Research Funding; Roche: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Elsevier: Honoraria; Adecept Bio: Consultancy; Mirror Biologics: Consultancy; Genentech: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; National Marrow Donor Program: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Gerson Lerhman Group: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy. Pratz:AbbVie, Agios, Daiichi Sankyo, Millennium: Research Funding; AbbVie, Astellas, Boston BioMedical, BMS, Celgene, Novartis, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Servier.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. McCurdy:Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal